Product
HybriMore™ Hybridoma Culture Supplement (Protein-free)
This product is now under the brand name "Topcells".
Please visit www.topcells.com.tw for the latest information.
Highlights
- Increase cloning efficiency and cell survival rate
- Growth-promoting supplement with defined chemical components and concentration
- Better signal-to-noise ratio of hybridoma supernatant for mAb screening
Generation of mAb Through Hybridoma Technology with HybriMore Cell Culture Supplement
- For the best efficiency, use HybriMore from post-cell fusion to antibody production.
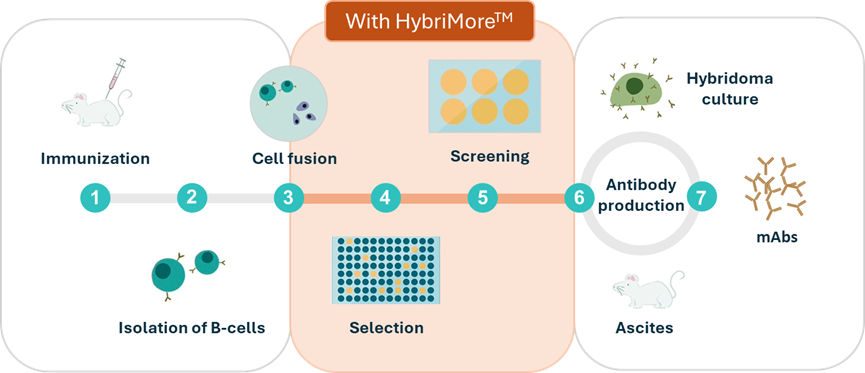
Preparation of hybridoma cells (general protocol):
1. The BALB /cJ mice were immunized with the desired antigen.
2. Mouse splenocytes were fused with myeloma cells.
3. Fused cells were gently resuspended in DMEM containing the desired concentration of fetal bovine serum, HAT, and HybriMoreTM.
4. Supernatants of hybridomas in 96-well plates were screened by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
5. Selected hybridoma clones were isolated by limited dilution.
6. The mAbs were obtained from hybridoma culture or mouse ascites.
7. Monoclonal antibodies were purified on Protein G-Sepharose columns.
Order Information
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Description |
| HB01-1L | HybriMore™ Hybridoma Culture Supplement* |
Lyophilized powder for 1 L culture medium dilution |
*Previous name: HybriMore Hybridoma Cloning Factor
Product Detail
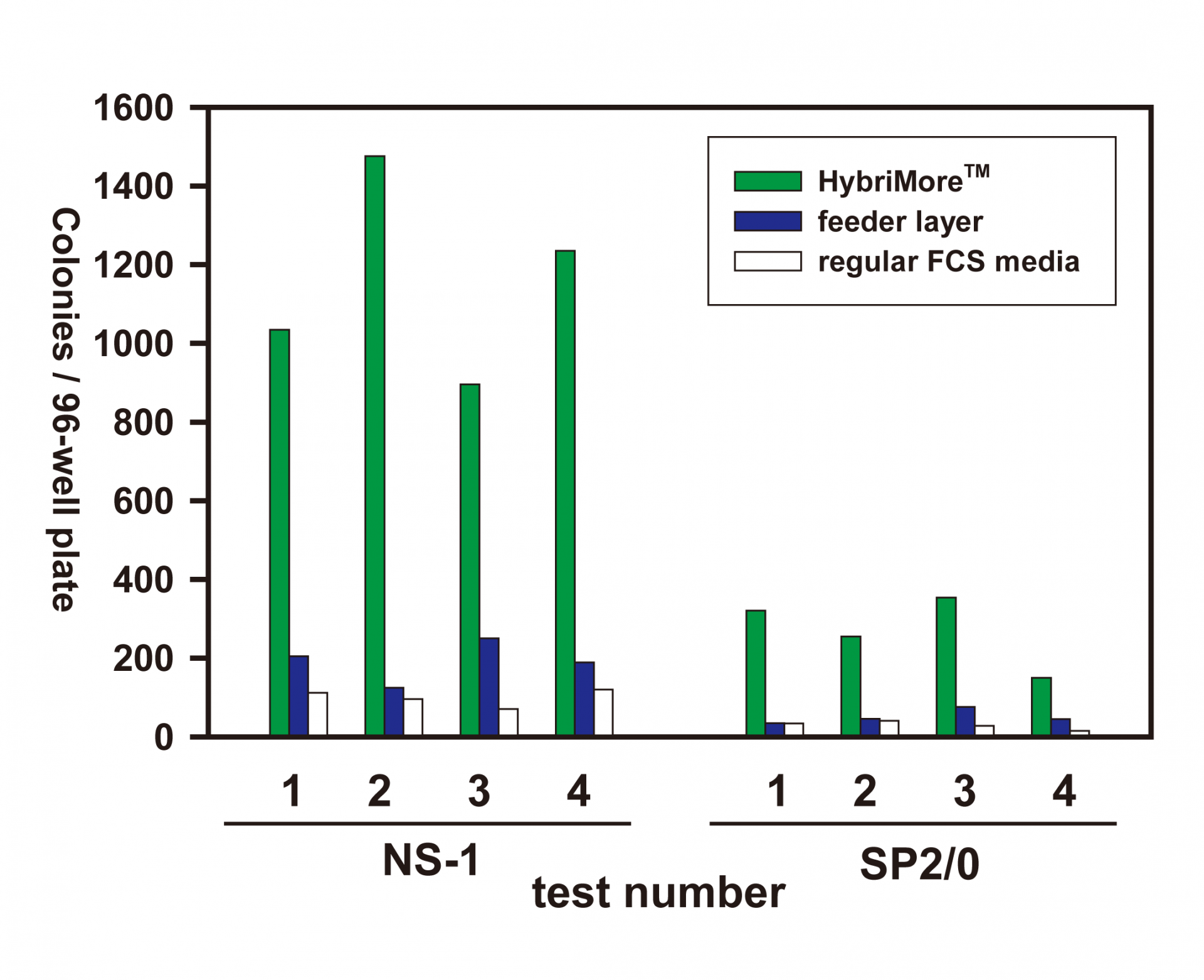
Figure 1. Comparison of the cloning efficiency of the newly fused hybridoma cells.
The newly PEG fused hybridoma cells were plated into a 96-well plate containing FCS media with HybriMore™ (green bars), FCS media with feeder layer (blue bars), or regular FCS media (white bars). Hybridoma cells were subject to HAT selection 14 days after cell fusion. The numbers of viable hybridoma colonies were visually counted under a microscope. Two mouse myeloma fusion partners, NS-1 and SP2/0, were evaluated by four independent fusion experiments with freshly prepared mouse spleens.
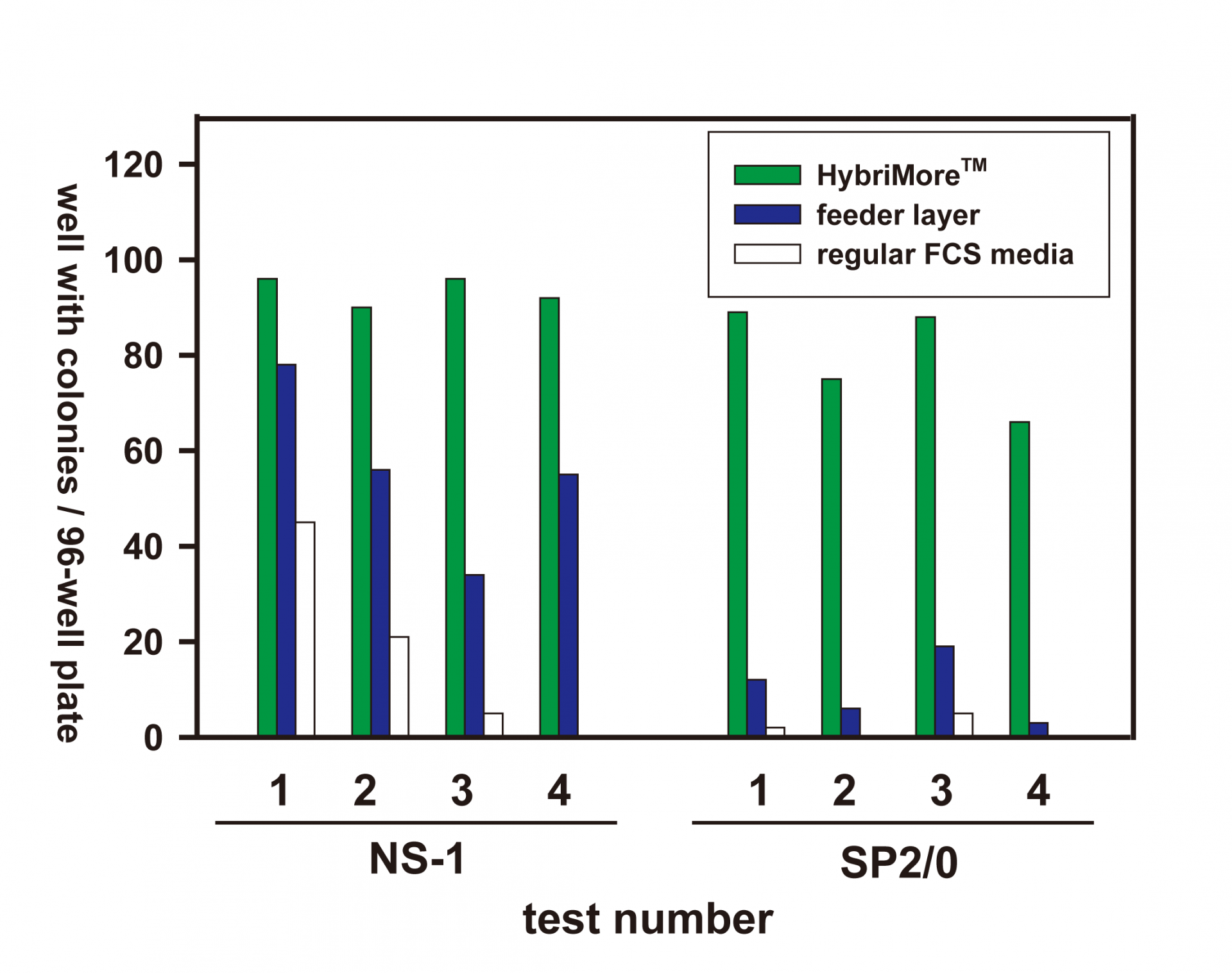
Figure 2. Comparison of the successful rate of monoclonizing hybridoma cells.
Eight clones of hybridoma cells from NS-1 or SP2/0 fusion partners were monoclonized in the media containing FCS media with HybriMore™ (green bars), FCS media with feeder layer (blue bars), or regular FCS media (white bars). The numbers of viable hybridoma colonies in a well were visually counted under a microscope.
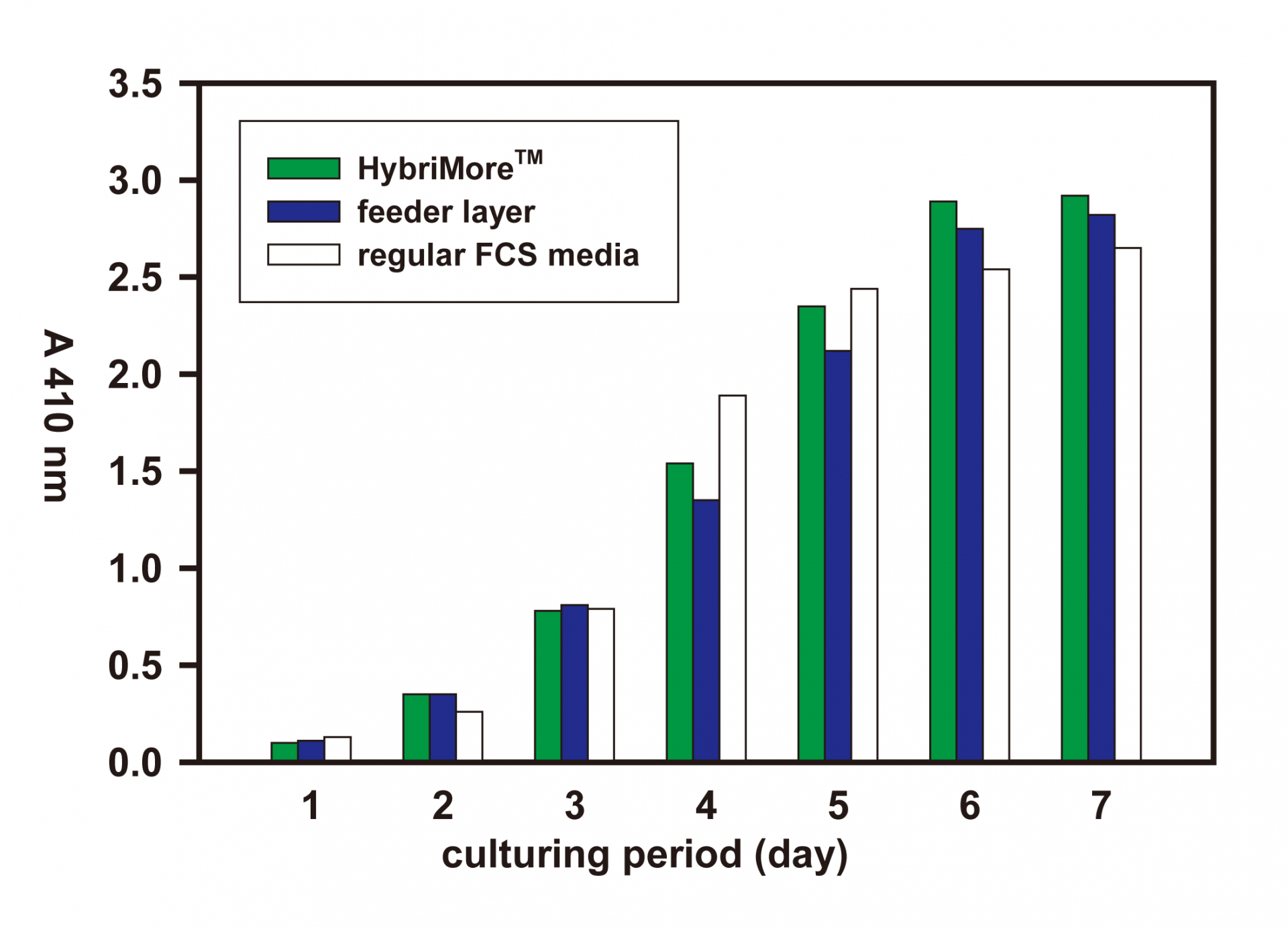
Figure 3. Comparison of the titers of secreting Ab.
A clone of hybridoma cells (anti-human transferrin, L3B5) was cultured in the media containing FCS media with HybriMore (green bars), FCS media with feeder layer (blue bars), or regular FCS media (white bars) for seven days. The supernatants were harvested and examined by the titer of secreting Ab by ELISA assay.
Reference
- Li, CJ., Huang, PH., Chen, HW. et al. Development and characterization of mouse monoclonal antibodies targeting to distinct epitopes of Zika virus envelope protein for specific detection of Zika virus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol (2021).
- Lai, Guan-Chun, et al. "Neutralization or enhancement of SARS-CoV-2 infection by a monoclonal antibody targeting a specific epitope in the spike receptor-binding domain." Antiviral Research 200 (2022): 105290.
- Su, Shih-Chieh, et al. "Structure-guided antibody cocktail for prevention and treatment of COVID-19." PLoS Pathogens 17.10 (2021): e1009704.
- Lu, Ruei-Min, et al. "Monoclonal antibodies against nucleocapsid protein of SARS-CoV-2 variants for detection of COVID-19." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22.22 (2021): 12412.
- Ko, Shih-Han, et al. "Monoclonal antibodies against S2 subunit of spike protein exhibit broad reactivity toward SARS-CoV-2 variants." Journal of Biomedical Science 29.1 (2022): 108.