Product
Protein Quantification
Dual-Range™ BCA Protein Assay Kit is the most used protein assay method. It based on bicinchoninic acid (BCA) for the colorimetric detection and quantitation of total protein in the 5–2,000 μg/mL concentration range. Like the Lowry method, the assay relies on the reduction of Cu2+ ions by protein. The Cu+ thus formed is detected by conversion into a violet-colored substance by reaction with bicinchoninate. Dual-Range™ BCA Protein Assay Kit is compatible with many detergents but not compatible with reducing agents such as DTT,DTE, and 2-Mercaptoethanol etc.
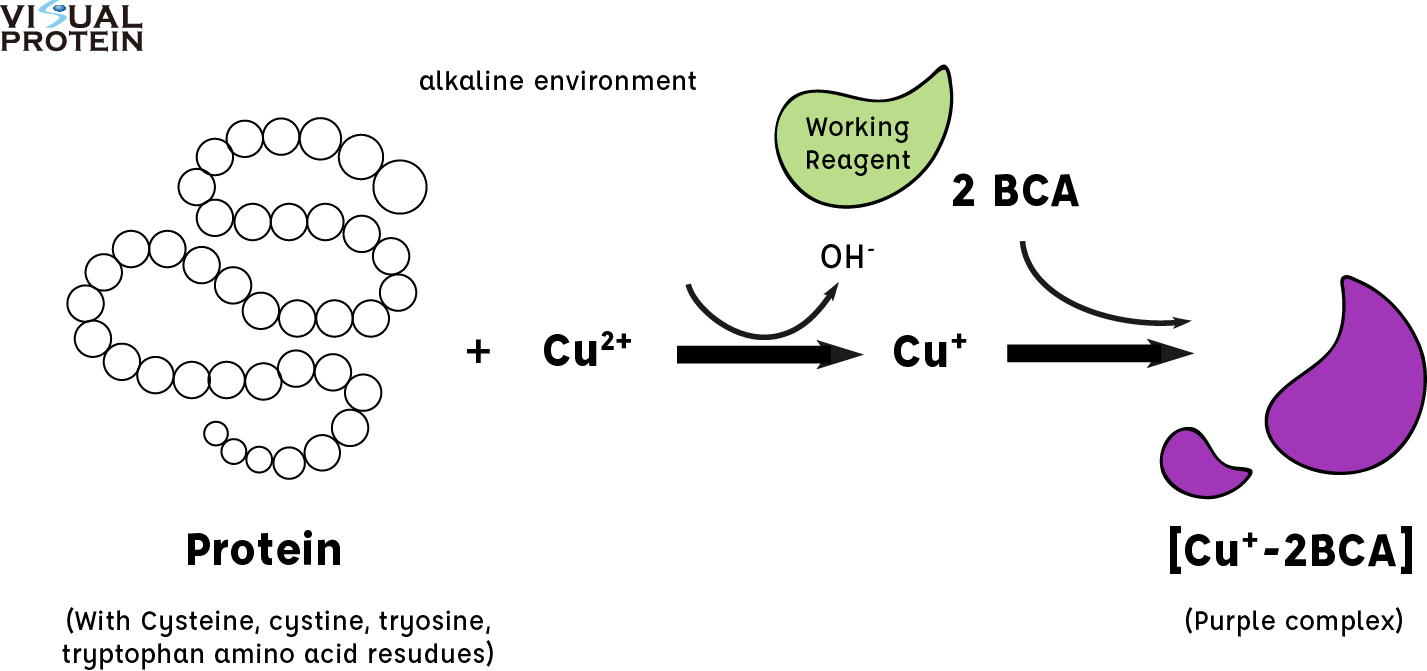
The BCA protein assay is based on a reduction of Cu2+ to Cu+ by proteins in alkaline solution with a sensitive and specific colorimetric detection of Cu+ by bicinchoninic acid (BCA). Two molecules of BCA chelate with each Cu+ and making the reduced copper from apple green to purple complex with strong absorbance at 562 nm.
Special Characteristic :
- Broad linear range: with standard protocol for 20-2000 μg/mL and enhanced protocol for 5-250 μg/mL
- Compatible: unaffected by typical concentrations of most ionic and nonionic detergents
Order Information :
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Description |
| BC03-500 |
Dual-Range™ BCA Protein Assay Kit |
1 kit 500mL Reagent A + 12 mL Reagent B + 10mL BSA (2mg/mL) For making 2500 microplate assays |
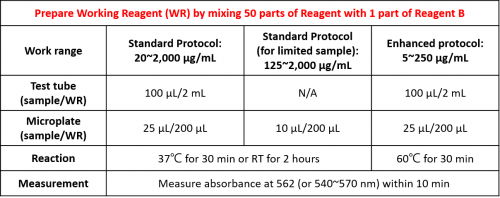
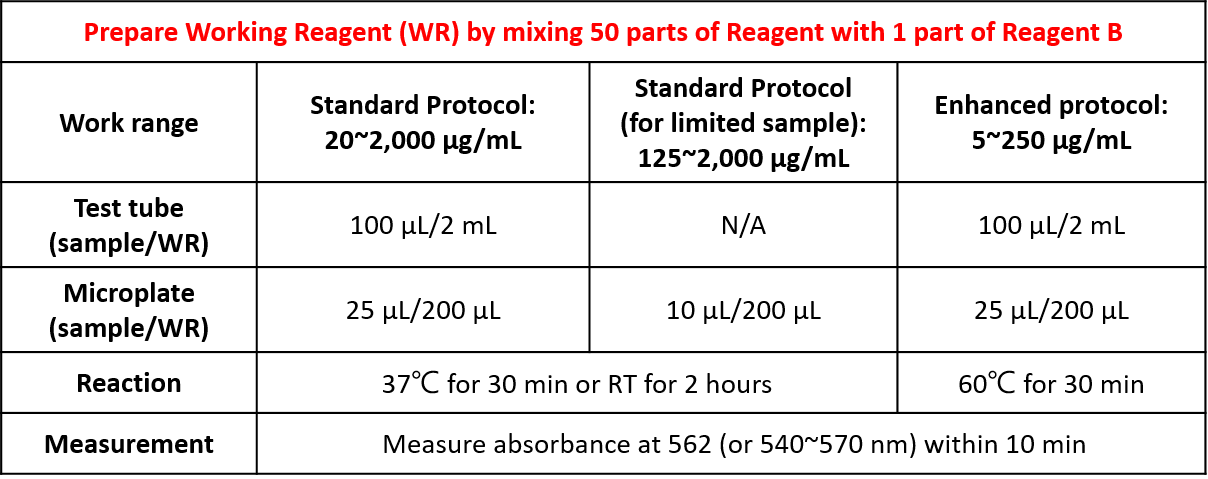
Quick Instructions:
Product Detail :
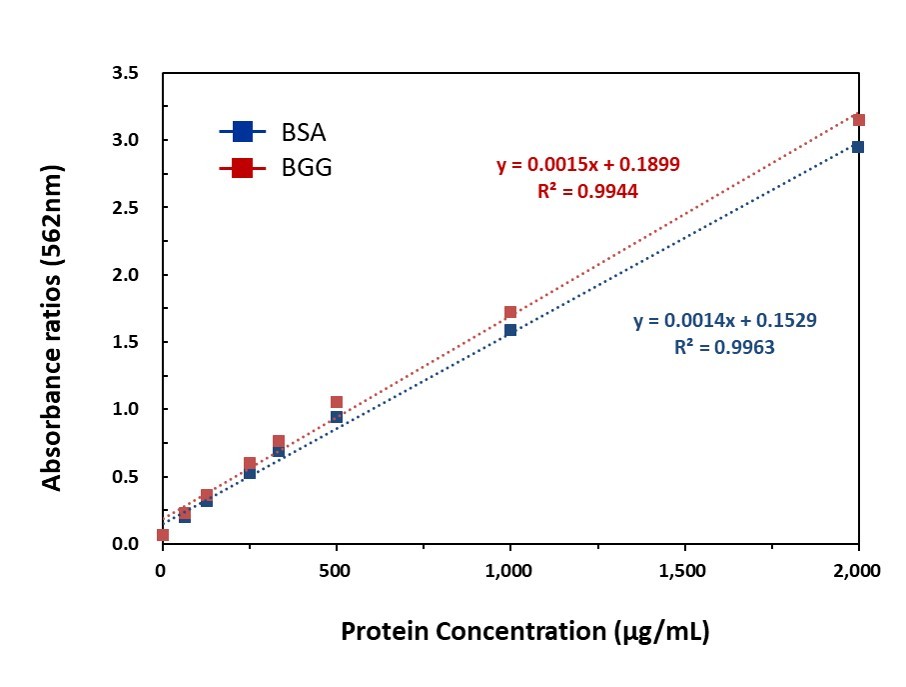
Figure 1. Standard curve of bovine serum albumin (BSA) and bovine gamma globulin (BGG) by using microplate procedure (37°C for 30mins).
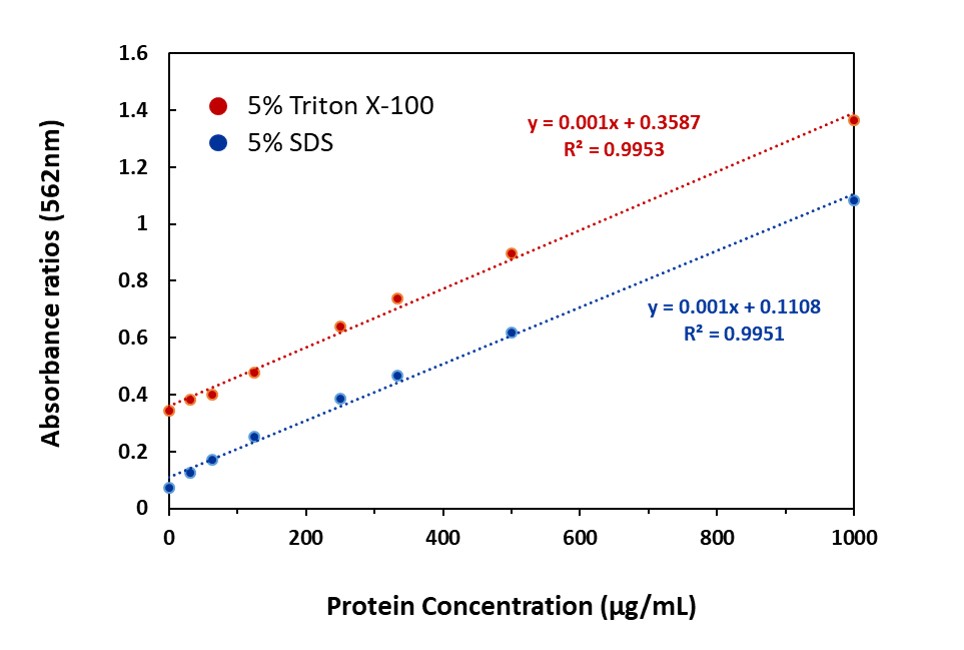
Figure 2. Standard curve of BSA with 5% Triton X-100 or 8% SDS by using microplate procedure (37°C for 30mins).
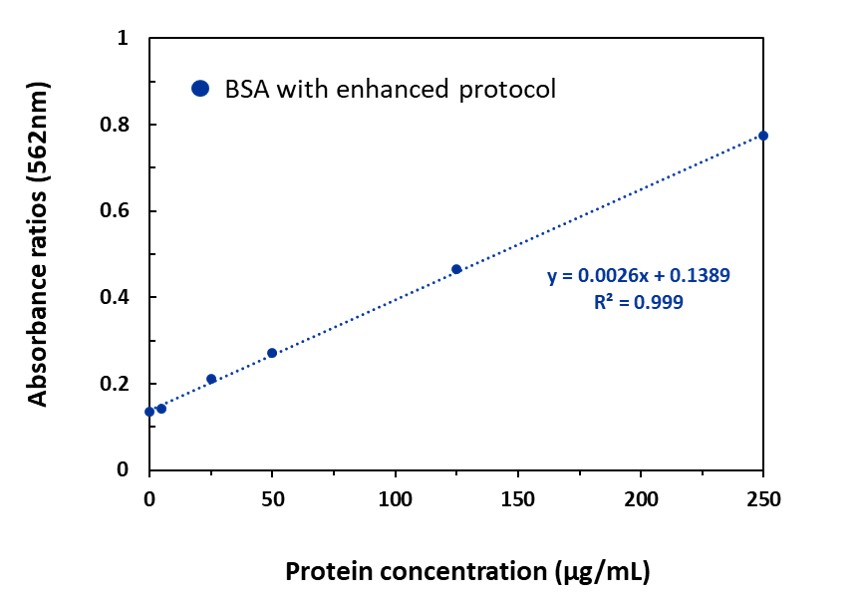
Figure 3. Standard curve of BSA by using microplate procedure by using microplate procedure with enhanced protocol (60°C for 30 mins).
Reference:
1. Young, Guang-Huar, et al. "The functional role of hemojuvelin in acute ischemic stroke." Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism (2019): 0271678X19861448.
2. Chen, Sheng-Yi, et al. "Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities and bioactive compounds of the leaves of Trichodesma khasianum clarke." Industrial Crops and Products 151 (2020): 112447.
3. Wang, Guan-Yu, et al. "Protective effect of rosmarinic acid-rich Trichodesma khasianum Clarke leaves against ethanol-induced gastric mucosal injury in vitro and in vivo." Phytomedicine (2020): 153382.
4. Hsu, Jen‐Ying, et al. "Aqueous extract from Pepino (Solanum muricatum Ait.) leaves ameliorated insulin resistance, hyperlipidemia, and hyperglycemia in mice with metabolic syndrome." Journal of Food Biochemistry 44.12 (2020): e13518.
5. Yang, Kai-Chiang, et al. "Effect of thermal treatments on the structural change and the hemostatic property of hair extracted proteins." Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 190 (2020): 110951.
6. Naito, Yoshisuke, et al. "Deterioration of Myofibrils Affected by Experimental Partial Immobilization in a Septic Rat Model." Journal of St. Marianna University 11.2 (2020): 61-72.
7. Young, Guang‐Huar, et al. "Modulation of adenine phosphoribosyltransferase‐mediated salvage pathway to accelerate diabetic wound healing." The FASEB Journal 35.3 (2021): e21296.
8. Leyton, Esteban, et al. "DEF8 and Autophagy-Associated Genes are Altered in Mild Cognitive Impairment, Probable Alzheimer’s Disease Patients and a Transgenic Model of the Disease." Journal of Alzheimer's Disease Preprint (2021): 1-16.
9. Hsu, Jen-Ying, et al. "Aqueous Extract of Pepino Leaves Ameliorates Palmitic Acid-Induced Hepatocellular Lipotoxicity via Inhibition of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Apoptosis." Antioxidants 10.6 (2021): 903.
10. Chen, Hong, et al. "Promoting effects of MiR-135b on human multiple myeloma cells via regulation of the Wnt/β-catenin/Versican signaling pathway." Cytokine 142 (2021): 155495.
11. Chen, Ying-Yin, et al. "4‑Acetylantroquinonol B enhances cell death and inhibits autophagy by downregulating the PI3K/Akt/MDR1 pathway in gemcitabine‑resistant pancreatic cancer cells." Oncology Letters 23.4 (2022): 1-13.