Product
Western Blotting
Highlights:
- Very High signal sensitivity: detection of target protein at the low-femtogram level
- Long duration: signal duration up to 12 hours
- Long shelf life: 18 months long at 4℃
Order Information:
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Description |
| LF24-100 | LumiFlash™ Femto Chemiluminescent Substrate, HRP System |
50mL Solution A + 50mL Solution B |
Product Detail:
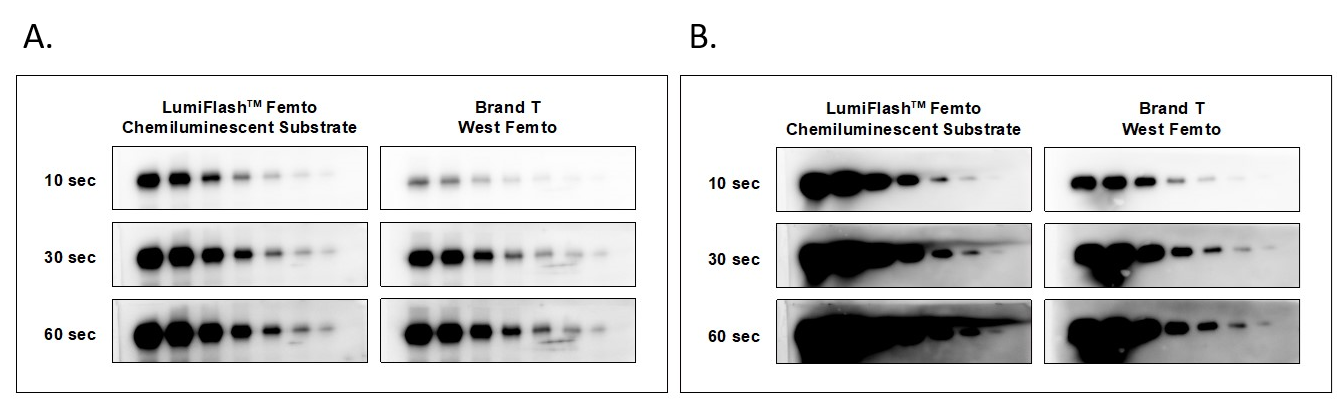
Figure 1. Western blotting image of LumiFlash™ Femto Chemiluminescent Substrate, HRP System.
Hela cell lysate with 1/2 serial dilution from 7 µg was separated by 12.5% SDS-PAGE. The proteins were transferred to PVDF and blocked for 1 min at room temperature with BlockPRO™ 1 Min (#BM01-500). (A) The blot was probed at 1:2,500 with Anti-Akt antibody (#4691, Cell Signaling Technology). (B) The blot was probed at 1:10,000 with Anti-GAPDH antibody (#ab8245, Abcam). A HRP-conjugated secondary antibody was applied and developed with LumiFlash™ Femto Chemiluminescent Substrate (#LF24-100). All blots were simultaneously exposed for 10 seconds, 30 seconds, and 60 seconds using ChemLux SPX-600 imaging system.
LumiFlash™ Series:

Reference:
1. Huang, Yen-Wen, et al. "2, 3, 5, 4′-tetrahydroxystilbene-2-ObD-glucoside triggers the pluripotent-like possibility of dental pulp stem cells by activating the JAK2/STAT3 axis: Preliminary observations." Journal of Dental Sciences (2020). Link
2. Mou D-F, Chen W-T, Li W-H, Chen T-C, Tseng C-H, Huang L-H, et al. (2021) Transmission mode of watermelon silver mottle virus by Thrips palmi. PLoS ONE 16(3): e0247500. Link
3. Lin, Yuh-Charn, et al. "SCUBE3 loss-of-function causes a recognizable recessive developmental disorder due to defective bone morphogenetic protein signaling." The American Journal of Human Genetics 108.1 (2021): 115-133. Link
